Product Category Rules at the service of sustainability
The last two years have seen a substantial growth in the publications of Environmental Product Declarations (EPD) and in requests for the creation and development of new Product Category Rules (PCR) in different sectors. The main tow was ENEL S.p.A. which, with its policy of enhancing the supply chain, has made a significant contribution to growth in the electricity sector of PCR and EPD, but there has also been an increasingly deep interest on the part of businesses, companies and universities.
Since PCRs are essential documents that provide the rules, requirements and guidelines for developing EPDs for a specific product category, the analysis of the context leads to highlight an increasingly strong diversification of the areas of application of EPDs and of a market increasingly attentive to sustainability issues.
The growth of PCRs in the EPDItaly system can be summarized in the following graph:
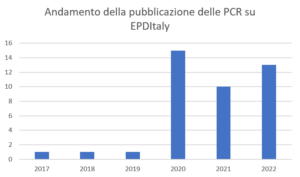
Since the acronym PCR has now become of daily use, it is good to remember the process that leads to the definition of these important documents, which provide producers with all the tools to undertake an EPD certification process with the aim of operating in a perspective of increasing environmental sustainability.
The steps for creating a PCR
The main steps in the development of new PCRs, within EPDItaly, comply with the requirements of ISO / TS 14027:
- Announcement of the intention to develop a PCR. EPDItaly informs interested parties of the launch of the initiative aimed at developing the PCR. In order to make the PCR a document shared by the various competing operators in the same product category, it is important that the calculation rules and the hypotheses included in the PCR are the result of teamwork. Therefore it is necessary to request the cooperation of several subjects, potentially interested in the product under study.
- Creation of the PCR Committee. The main task of this Committee, formed by the proposer of the PCR and any Stakeholders referred to in point a), is to develop the PCR and submit the PCR to EPDItaly to be sent for public consultation.
- PCR creation. The PCR serves to define, within the category of products to which it refers, which rules in defining the system boundaries or which quality requirements in data collection must be respected in the LCA study used to prepare the EPD, as well as which ones must be the declared unit, otherwise called functional, taken as a reference and what information must be included in the EPD. In detail, the PCR will have to consider the elements specified in ISO / TS 14027.
- Appointment of the moderator. The PCR Committee appoints a competent person whose task is to provide the necessary support for a harmonious development of the PCRs, managing the comments received from the Stakeholders from the next phase.
- Public consultation. The public consultation phase serves to ensure that the main subjects involved in various capacities in the life cycle of the product category are informed of the publication of the PCR, in order to report their comments and proposals for amendments before the document is formalized as PCR in its final version. The public consultation phase usually lasts 30 days.
- Management of comments and review of the PCR. The comments received are screened by the moderator who provides for their possible implementation by making the necessary changes to the PCR. The moderator keeps a history of the review of the comments and of the changes made. Once a consolidated version of the PCR is reached, the moderator submits it, together with the history, to the PCR Review Committee for final approval.
- Creation of the PCR Review Committee. The task of this Committee, third respect to EPDItaly and the proposer, is to verify that the process of drafting the PCR and managing the public consultation took place in accordance with what is specified in the EPDItaly Regulation and must ensure: compliance of the PCR with ISO 14025 and ISO / TS 14027;
that the methods required by the PCR are scientifically and technically valid;
that the requested data are appropriate. - Publication of the PCR. The PCR is made public with all the information necessary for its correct identification.
The Preliminary Validation
It is important to remember that, in order to facilitate the development of EPDs and with them the consolidation of the sensitivity of consumers and the market to the conscious purchase of products, also selected on the basis of their environmental performance, the development of EPDs is envisaged without a relative PCR, under certain conditions.
EPDItaly foresees that an EPD can be published, in the absence of PCR, as Preliminary Validation. The duration of this type of EPD is set at 18 months, without renewal. Preliminary Validation represents the first step to develop a PCR, as it can allow the birth of a discussion between the various Stakeholders. To obtain the Preliminary Validation through the validation of a Certification Body, it is necessary that the EPD responds in the minimum format and content to the provisions of the EPDItaly Regulation and that the LCA study is developed according to the ISO 14040 and 14044 and EN 15804 standards. for construction products.
EPDItaly technicians are available for any doubts on the above issues and to deepen the PCR development process.

